Carotid Artery Disease Treatment Options
Carotid Artery Disease
Treatment Options
Carotid Artery Disease Treatment Options
Carotid artery disease is a significant cause of the 800,000+ strokes that impact people in the US each year.
Carotid Artery Stenosis
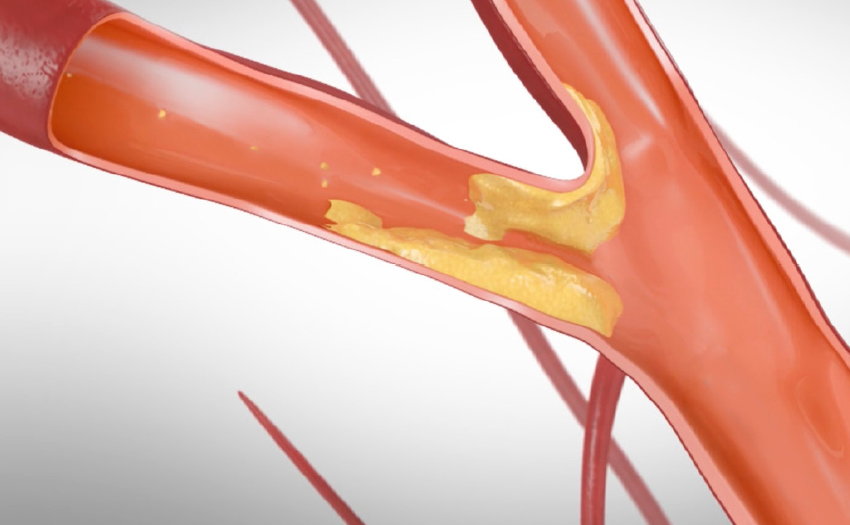
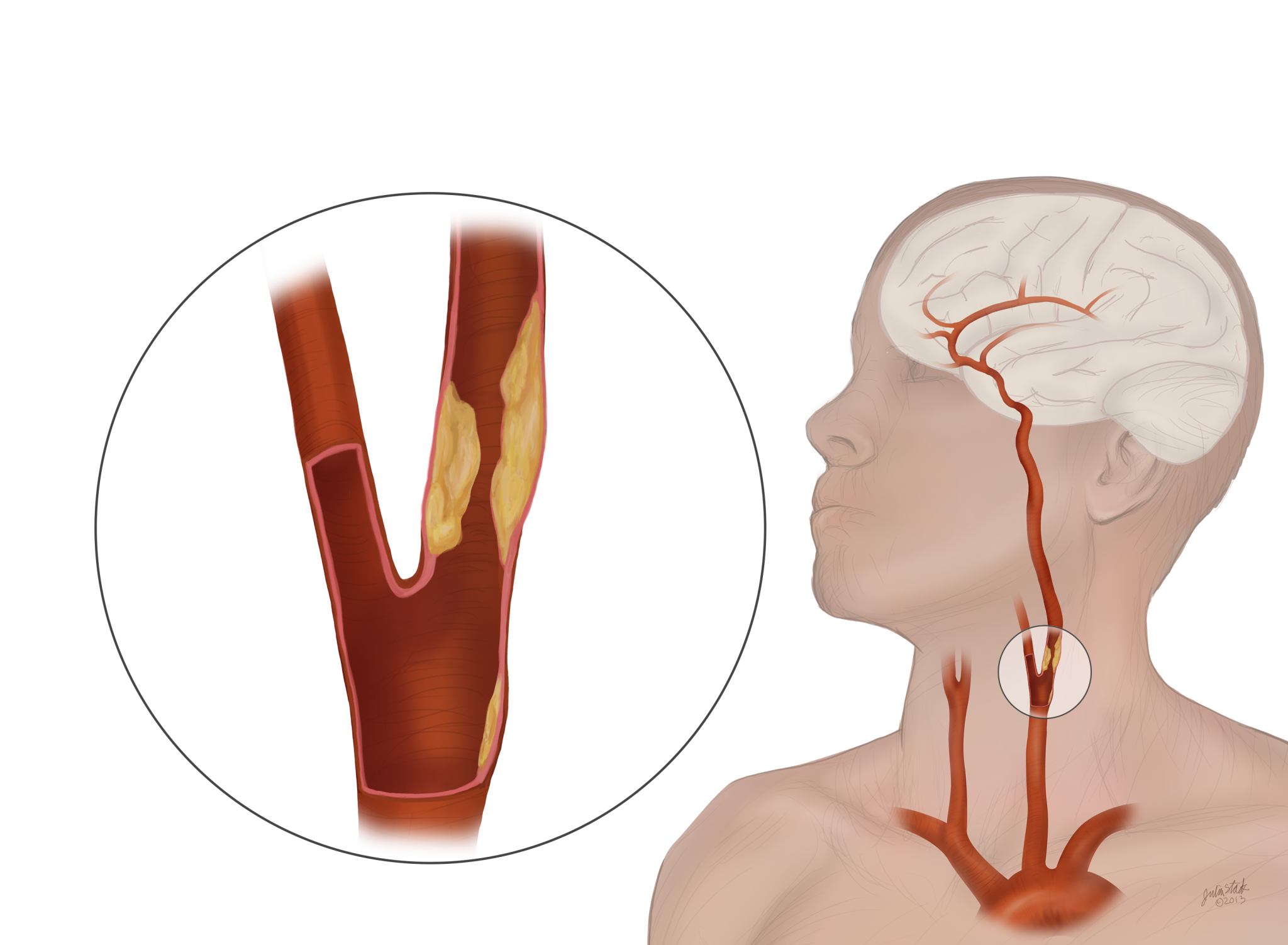
Diagnosing Carotid Artery Disease
Diagnosing Carotid Artery Disease

The Risk of Stroke

You may be at risk of carotid artery disease related stroke if you have two or more of the following:

High cholesterol

High blood pressure

Tobacco smoking

Family history
You may be at risk of carotid artery disease related stroke if you have two or more of the following:

High cholesterol

High blood pressure

Tobacco smoking

Family history
Carotid Artery Disease Symptoms
Carotid artery disease develops slowly. Often called the silent killer, the first symptom for a patient at risk for stroke is a stroke itself or a “mini-stroke” called a transient ischemic attack (TIA). A TIA is a temporary stroke that resolves itself in 24 hours or less. It is considered a warning sign for a full-blown stroke. If someone is having stroke-like symptoms (weakness/numbness on one side, loss of eyesight/speech, garbled speech, dizziness or fainting), they should seek immediate medical attention and be evaluated for carotid blockage and stenosis. If you suspect a stroke, remember to act F.A.S.T.

Face Drooping

Arm Weakness

Slurred Speech

Time to Call 9-1-1
Carotid Artery Disease Symptoms
Carotid artery disease develops slowly. Often called the silent killer, the first symptom for a patient at risk for stroke is a stroke itself or a “mini-stroke” called a transient ischemic attack (TIA). A TIA is a temporary stroke that resolves itself in 24 hours or less. It is considered a warning sign for a full-blown stroke. If someone is having stroke-like symptoms (weakness/numbness on one side, loss of eyesight/speech, garbled speech, dizziness or fainting), they should seek immediate medical attention and be evaluated for carotid artery blockage and stenosis. If you suspect a stroke, remember to act F.A.S.T.

Face Drooping

Arm Weakness

Slurred Speech
